Student Union
Mask Mandates Return to US College Campuses as Cases Rise
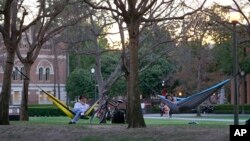
The final weeks of the college school year have been disrupted yet again by COVID-19 as universities bring back mask mandates, switch to online classes and scale back large gatherings in response to upticks in coronavirus infections.
Colleges in Washington, D.C., New York, Pennsylvania, Massachusetts, Connecticut and Texas have reimposed a range of virus measures, with Howard University moving to remote learning amid a surge in cases in the nation's capital.
This is the third straight academic year that has been upended by COVID-19, meaning soon-to-be seniors have yet to experience a normal college year.
"I feel like last summer it was everyone was like, 'Oh, this is it. We're nearing the tail end,'" recalled Nina Heller, a junior at American University in Washington D.C., where administrators brought back a mask mandate about a month after lifting it. "And then that didn't quite happen, and now we're here at summer again, and there's kind of no end."
Mandates were shed widely in the wake of spring break as case numbers dropped following a winter surge fueled by the omicron variant. But several Northeast cities have seen a rise in cases and hospitalizations in recent weeks, as the BA.2 subvariant of the omicron variant continues to rapidly spread throughout the U.S.
"As much as we would like to move on and think that the pandemic is over, and I think we all would like that to happen at this point, it's wishful thinking," said Anita Barkin, co-chair of a COVID-19 task force for the American College Health Association. "The pandemic is still with us."
COVID-19 had eased so much at Williams College that the private liberal arts school in Massachusetts allowed professors to decide whether to require masks in their classes early last week. But just days later, with cases rising, it reinstated an indoor mask mandate, which was even stricter than what had been in place before.
"I think students are really feeling like people they know are dropping like flies," said junior Kitt Urdang, who's had a half-dozen friends test positive in recent days. "There's definitely been a lot more uncertainty than there's been on campus since COVID hit."
Philadelphia recently brought back its mask mandate, leading the University of Pennsylvania and Temple University to again require them starting Monday, April 25. Although the city ended the mandate Thursday, April 21, the colleges haven't made any changes.
In Washington, D.C., Howard University's main campus, affectionately dubbed "The Hilltop" by students and alums, was largely quiet this week, with many students taking classes and exams from home. The academic year is coming to a muted end as rising virus numbers prompted administrators to abruptly shift back to online education.
The city's COVID infection rate has more than doubled in April. Besides American, Georgetown and George Washington University also reinstated their indoor mask mandates. But Howard is the only one that has moved away from in-person instruction.
The spring semester ends Friday, with final exams for most students starting next week. Administrators have promised an update on what this means for the May 7 commencement ceremony.
"I don't think people are super unhappy about wearing masks," said Lia DeGroot, a George Washington senior who never shed her mask during the single week the mandate was lifted at her school. "Of all of the things that the pandemic has disrupted, I think wearing masks is, you know, a relatively small thing to do. I think that's kind of the mindset that a lot of students have."
In nearby Baltimore, Maryland, Johns Hopkins University announced this month that it was testing all undergraduate students twice weekly through Friday, noting a steep rise in cases. The school also said masks would be required not just in classrooms, but in places like residence hall common areas.
In Houston, Rice University announced earlier this month that students should resume wearing masks in classrooms, citing an uptick in cases on campus. Large college parties also were canceled.
New Mexico State University took a different tack, announcing Monday that all students on campus must be fully vaccinated against COVID-19 by July 1, ending the option of submitting weekly tests as an alternative.
One of the few counties still identified by the CDC as having high spread is home to New York's Syracuse University, which announced Monday that it would again require masks in classrooms.
J. Michael Haynie, the school's vice chancellor for strategic initiatives and innovation, said in a letter that "it is important that we take reasonable action to minimize the impact of COVID infections" with finals and commencement fast approaching.
The University of Rochester in upstate New York, the University of Connecticut, Bowdoin College in Brunswick, Maine, and Columbia University in New York City took a similar approach. Many, like Columbia, noted that their surveillance testing programs were finding more cases.
While many students were eager to mask up, grumbling was emerging.
"We're to the point where we're tired of masks," said Neeraj Sudhakar, a Columbia grad student studying financial engineering. "We probably have a 99% vaccination rate, so at this point I think we just need to move on with the pandemic and treat it as endemic rather than going back to what we were doing the past two years."
See all News Updates of the Day
- By VOA News
International students discuss US campus culture shock

International students at De Anza College in Cupertino, California, talked about culture shock in an article in La Voz News, the student newspaper.
"It felt like a major culture shock. Everything was so different, from academics to mannerism," said a student from Mexico.
Read the full story here.
These are the most expensive schools in the US

High tuition costs along with housing and food expenses can add up for students at U.S. colleges and universities.
MSNBC looked at the most expensive schools in the country, with one costing more than $500,000 for a bachelor’s degree. (June 2024)
Uzbekistan students admitted into top US universities

Students from Uzbekistan are among the international students admitted to top colleges and universities in recent years.
Gazata.uz profiled some of the Uzbekistan students attending Harvard, Brown, Princeton and other U.S. universities. (June 2024)
- By Stella Hsu
Reports of visa checks, deportations worry Chinese STEM students in US

Geopolitical tensions and growing competition in tech between the United States and China appear to be spilling over into academia despite commitments from the world’s two biggest economies to boost people-to-people exchanges.
The United States remains the top choice for Chinese students seeking to study abroad with nearly 300,000 studying in American colleges and universities during the 2022-2023 school year. But reports of some cases that students and professors are facing extra scrutiny while passing through immigration and the deportation of others are raising concerns.
For Chen Xiaojin, a doctoral student studying semiconductor materials at a university in the Washington, D.C., metropolitan area, it has been six years since she returned to her hometown of Beijing.
At first, it was the COVID-19 pandemic that kept her from going home. But over the past two years, she has been deterred by accounts of Chinese students majoring in science and engineering being required to reapply for their visas upon returning to China.
She also says she is worried by reports over the past six months of Chinese students being deported, even at nearby Dulles Airport.
"My current research is relatively sensitive, and my boss [adviser] is getting funds from the U.S. Department of Defense, making it even more sensitive,” she told VOA. "I am afraid that I won't be able to return after I go back [to China]."
Chen says that if she did return to China, she would have to apply for a new visa.
In a report late last month, Bloomberg said it had found at least 20 Chinese students and scholars with valid visas who were deported at U.S. Customs since November and barred from reentry. The U.S. Customs and Border Protection Agency does not release relevant data.
Immigration attorney Dan Berger represented one Chinese student who was deported late last year. He tells VOA Mandarin that the student studied biological sciences at Yale University and was about to complete her doctorate.
She visited her family in China and got a new visa but was deported by customs at Dulles Airport and barred from reentering the country for five years. Berger said he did not see anything suspicious in the transcript of the conversation between the student and the customs officer.
"We have seen what seems like a pattern over the last six months of Chinese PhD students being turned around…. more than I've seen in quite a while," he said.
Matthew Brazil, a fellow at the Jamestown Foundation, said neither country seems willing to explain the situation. However, he believes that in most cases, the United States must have valid reasons for blocking visa holders from entering the country.
In some cases, the student’s background may not match what is written on the visa application. In other cases, customs agents may also find something that the State Department missed, and once they see it, they are responsible for taking action.
"I wish the Chinese side would be specific about their students who were refused entry,” he said. “The fact that both sides are mum on details and that the Chinese side is engaged with the usual angry rhetoric means that each has security concerns. And that says to me that there was good reason for the U.S. to stop these particular applicants."
Brazil also sees a connection between the entry denials and export control regulations issued by the United States in October 2022 that restrict China's ability to obtain advanced computing chips, develop and maintain supercomputers, and manufacture advanced semiconductors.
U.S. Customs and Border Protection is one of the law enforcement agencies authorized to investigate violations of export control regulations, he said.
"Beijing's intelligence agencies are known to focus attention on PRC [People's Republic of China] students and scientists headed abroad who study or work on dual-use technologies controlled under the Export Administration Act — compelling Chinese students and scientists to report on what they've learned when they return to China on holiday,” he said. “This has been true for decades."
Bill Drexel, a fellow for the Technology and National Security Program at the Center for a New American Security, said the U.S. government did find some cases where students tried to steal strategic technology for China.
"I think it would both not be surprising that they found some really questionable or incriminating evidence for some students,” he said. “It would also not be surprising if, in their hunt for really solid evidence, they also may have made some mistakes on other students.”
Drexel adds that “it’s just kind of an unfortunate fact of the time that we live in and the tactics that the CCP uses when it comes to these measures."
In a post on X in early May, U.S. ambassador to China Nicholas Burns tried to dispel concerns about visas and entry to the United States for students and scholars. In the post, he said "99.9% of Chinese students holding visas encounter no issues upon entering the United States.”
In an interview with The Wall Street Journal Monday, Burns said it is China that is making it impossible to promote people-to-people ties. Burns told the Journal that students attending events sponsored by the United States in China have been interrogated and intimidated.
He also said that since U.S. President Joe Biden and China’s leader Xi Jinping held their summit in San Francisco last year, China’s Ministry of State Security and other agencies had interfered with Chinese citizens’ participation at some 61 events.
At a regular briefing on Wednesday, Chinese Foreign Ministry spokesperson Mao Ning dismissed those accusations, saying that they did not “reflect reality" and that went against key understandings reached by both countries’ presidents in San Francisco.
“The United States, under the pretext of 'national security,' unjustifiably harasses, interrogates, and deports Chinese students in the U.S., causing them significant harm and creating a severe chilling effect,” Mao said. “The image of the United States in the minds of the Chinese people fundamentally depends on the actions of the United States itself.”
Drexel said he believes Burns’ comments about visas and students' willingness to study in the U.S. still ring true.
“On balance, it's still the case that American universities are overwhelmingly warm towards Chinese students and want them in large numbers," he said.
However, Berger, the immigration lawyer, is concerned about the chilling effect recent cases involving Chinese students could have.
"In general, we are being more careful about advising Chinese graduate students in STEM fields about traveling and letting them know that there is some small risk,” he said.
Even though the risk is small, it does seem to be real at the moment, he said.
Adrianna Zhang contributed to this report.
US federal judge blocks new regulation targeting for-profit colleges

A federal judge in Texas has blocked a regulatory provision targeting for-profit colleges that was scheduled to take effect in July 2024.
Times Higher Education reports that the rule, which would affect student loans, was challenged by for-profit institutions. (June 2024)










