It's not an uncommon experience to feel like you are not alone... even when you know you are. It's a foundation for many scary movies. But many people sense an unseen presence outside the movie theater.
The skeptic says it's all in your mind. True enough, a new study says, but that doesn't mean it's not real.
According to the new research, the feeling of not being alone, or of being watched is real. It's what happens when your brain gets confused with the information it's getting from your senses. So, while an invisible presence isn't really there, the brain creates a 'ghost' to help it reconcile the sensory input. Researchers in Switzerland proved it by recreating that eerie sensation in the lab. They say 'ghosts' may be triggered by intense physical stress or emotional shock, as well as by neurological and psychiatric disorders.
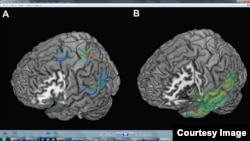
Scientists at the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology in Lausanne (EPFL) analyzed MRIs of 12 patients with brain disorders who reported experiencing these apparitions. They found disturbances in parts of the brain that deal with movement and the position of the body.
In the lab they recreated the dissonance with a device that sent mixed-up sensory-motor signals to healthy subjects. As the blind-folded participants manipulated a lever in front of them, a robotic hand touched their back. When it mimicked their movements exactly, they felt, oddly, that they were touching their own back. But when the researchers added just a slight delay between the participants' movement and the robot's, the people said they felt there was someone else standing behind them, touching them.
Writing in Current Biology, the researchers explain that the test subjects' brains no longer identified the tactile signals as belonging to their own body, interpreting them instead as something 'other' - that unseen presence. The findings could help explain the wide-spread phenomenon of guardian angels, ghosts and other apparitions.