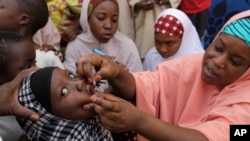
Nigeria’s difficult victory over polio faces a challenge as the poliovirus type 2 variant reemerges and the nation considers new measures to tackle the outbreak.
Nigeria eradicated wild polio in 2020, but more than 50 cases of the poliovirus type 2 variant were reported between January and May. Authorities and global partners met Wednesday in Abuja with northern traditional leaders to strengthen efforts against the disease, particularly in under-immunized areas.
Bill Gates, a key global funder of Nigeria's polio fight, said eradicating this strain is a top priority for the Gates Foundation.
"We do have this circulating variant, poliovirus type 2. The acronym is cVDPV2. ... Unfortunately, it's equally bad as the wild poliovirus,” Gates said. “It can paralyze or even kill children, and we still have work to do to get rid of this."
Efforts focus on improving surveillance and expanding vaccination coverage. The World Health Organization noted setbacks earlier this year, stressing the need for continuing vigilance.
"We are facing the challenge of interrupting transmission of significant variant poliovirus type 2,” said Walter Kazadi Mulombo, WHO country representative to Nigeria. “We nearly got there several months ago but then we experienced some setbacks."
Reluctance to take the vaccine, driven by religious and traditional beliefs, has hampered polio eradication efforts in Nigeria. However, northern traditional leaders have played a pivotal role in community outreach and health campaigns.
Muyi Aina, executive director of the Nigerian Primary Healthcare Development Agency, said traditional leaders have helped close the immunization gap in remote areas.
"The results we're getting are due largely to the commitment received from our revered traditional leaders,” Aina said. “For example, we had a 57% reduction in pending noncompliance from the April campaign, and we were able to vaccinate an additional 117,000 zero-plus children [newborns and older] across 14 states with the help of the traditional leaders."
Nigeria's routine vaccination efforts, including recent campaigns to immunize against the human papilloma virus have been lauded. However, the resurgence of poliovirus type 2 highlights the need for sustained immunization, especially in vulnerable regions.
Cristian Munduate, the UNICEF country representative, called for more collaboration.
"We need to accelerate with polio, but we also need to accelerate in line with all these effects to link more routine immunization to reach those children,” Munduate said. “To work and strengthen primary health care, we are very committed to at least having one primary health care [worker] fully equipped per ward."
Muhammadu Sa'ad Abubakar, the sultan of Sokoto, representing northern traditional rulers, reaffirmed their commitment to supporting vaccination efforts while thanking stakeholders.
"We are more concerned in the welfare of our people, so whoever is going to help us to help our people is part and parcel of us and is always welcomed,” Abubakar said.
Despite progress, the resurgence of poliovirus type 2 remains a serious threat. The Abuja meeting concluded with calls for stronger efforts, better surveillance, and continued collaboration between traditional leaders and health officials to ensure eradication.