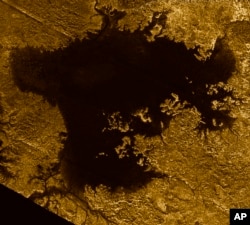
Scientists on Monday provided the most comprehensive look to date at one of the solar system's most exotic features: prime lakeside property in the northern polar region of Saturn's moon Titan — if you like lakes made of stuff like liquid methane.
Using data obtained by NASA's Cassini spacecraft before that mission ended in 2017 with a deliberate plunge into Saturn, the scientists found that some of frigid Titan's lakes of liquid hydrocarbons in this region are surprisingly deep while others may be shallow and seasonal.
Titan and Earth are the solar system's two places with standing bodies of liquid on the surface. Titan boasts lakes, rivers and seas of hydrocarbons: compounds of hydrogen and carbon like those that are the main components of petroleum and natural gas.
The researchers described land forms akin to mesas towering above the nearby landscape, topped with liquid lakes more than 300 feet (100 meters) deep comprised mainly of methane. The scientists suspect the lakes formed when surrounding bedrock chemically dissolved and collapsed, a process that occurs with a certain type of lake on Earth.
The scientists also described "phantom lakes" that during wintertime appeared to be wide but shallow ponds — perhaps only a few inches (cm) deep — but evaporated or drained into the surface by springtime, a process taking seven years on Titan.
The findings represented further evidence about Titan's hydrological cycle, with liquid hydrocarbons raining down from clouds, flowing across its surface and evaporating back into the sky. This is comparable to Earth's water cycle.
Because of Titan's complex chemistry and distinctive environments, scientists suspect it potentially could harbor life, in particular in its subsurface ocean of water, but possibly in the surface bodies of liquid hydrocarbons.
"Titan is a very fascinating object in the solar system, and every time we look carefully at the data we find out something new," California Institute of Technology planetary scientist Marco Mastrogiuseppe said.
Titan, with a diameter of 3,200 miles (5,150 km), is the solar system's second largest moon, behind only Jupiter's Ganymede. It is bigger than the planet Mercury.
"Titan is the most Earth-like body in the solar system. It has lakes, canyons, rivers, dune fields of organic sand particles about the same size as silica sand grains on Earth," Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory planetary scientist Shannon MacKenzie said.
The research was published in the journal Nature Astronomy.