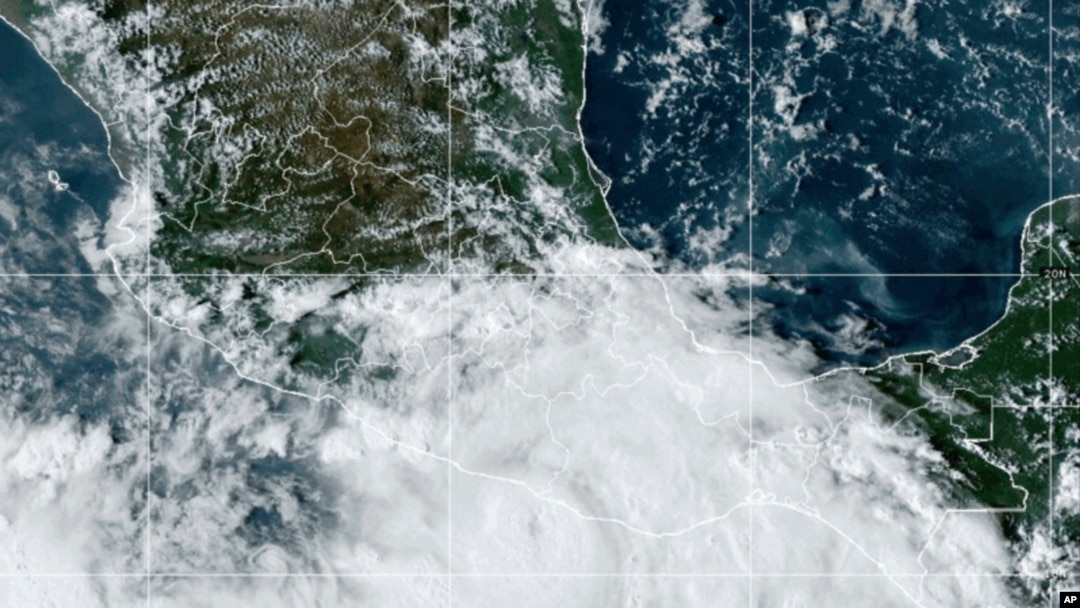
Tropical Storm John struck Mexico’s southern Pacific coast with life-threatening flood potential after growing into a major hurricane in a matter of hours.
It came ashore near the town of Punta Maldonado late Monday night as a Category 3 hurricane with maximum sustained winds of 120 mph (190 kph). It weakened back to tropical storm status early Tuesday with maximum sustained wind speeds of 70 mph (110 kph) and was expected to weaken rapidly.
Still, the United States National Hurricane Center warned that the storm’s slow pace and heavy rains could cause potentially catastrophic flash flooding and mudslides in some Mexican states.
“Seek higher ground, protect yourselves and do not forget that life is the most important thing; material things can be replaced. We are here,” Mexican President Andrés Manuel López Obrador wrote on the social media platform X.
The storm was expected to batter Punta Maldonado and the nearby tourist hubs Acapulco and Puerto Escondido before being weakened over the high terrain inland.
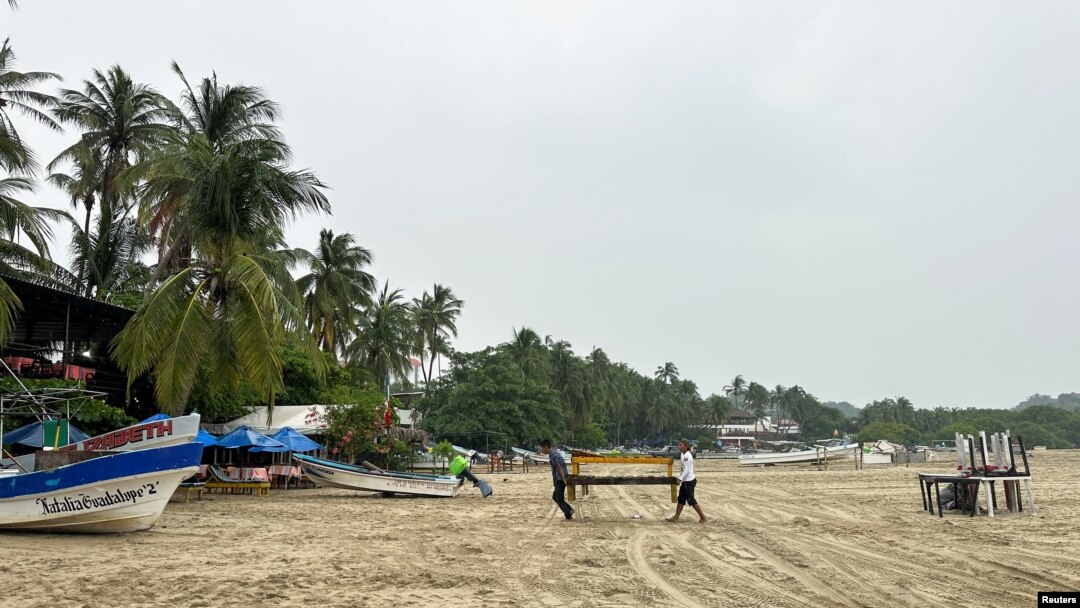

Residents carry wooden tables ahead of the arrival of Storm John, in Puerto Escondido, Oaxaca state, Mexico, Sept. 23, 2024.
The center said heavy rainfall over coastal southwest Mexico through the week was likely to cause “significant and possible catastrophic, life-threatening flash flooding and mudslides” in parts of Chiapas, Oaxaca, and Guerrero states.
Monday's unexpected surge in strength caught scientists, authorities and residents of the area by surprise, something AccuWeather Senior Meteorologist Matt Benz attributed to warmer oceans, which add fuel to hurricanes.
As a result, surprise surges in hurricanes' strength have become increasingly common, Benz said.
“These are storms that we haven’t really experienced before,” he said. “Rapid intensification has occurred more frequently in modern times as opposed to back in the historical record. So that’s telling us there’s something going on there.”
Residents were tense in Oaxaca’s coastal cities as the forecast shifted and authorities responded.
Laura Velázquez, the federal coordinator of civil protection, told residents of Pacific coastal cities they should evacuate their homes and head to shelters in order to “protect theirs and their family's lives.”
“It's very important that all citizens in the coastal zone … take preventive measures," Velázquez said.
Ana Aldai, a 33-year-old employee of a restaurant on the shores of the tourist hub Puerto Escondido, said businesses in the area began closing after authorities ordered the suspension of all work on the area's main beaches.
The governments of Guerrero and Oaxaca states said classes would be suspended Tuesday in a number of coastal zones.
Oaxaca's governor said the state government evacuated 3,000 people and set up 80 shelters. It also said it sent out 1,000 military and state personnel to address the emergency.
Videos on social media from Puerto Escondido showed flip-flop-clad tourists walking through heavy rain and fishers pulling their boats out of the water. Strong rains in previous days have already left some roads in the region in a precarious position.
The storm is bleak news for the region, which was walloped by Otis, a similar rapidly intensifying hurricane, in 2023.
Otis devastated the resort city of Acapulco, where residents had little warning of the strength of what was about to hit them. One of the most rapidly intensifying hurricanes ever seen, scientists at the time said it was a product of changing climate conditions.
Otis blew out power in the city for days, left bodies scattered on the coast and desperate family members searching for lost loved ones. Much of the city was left in a state of lawlessness and thousands scavenged in stores, scrambled for food and water.
The government of López Obrador received harsh criticism for its slow response to Otis, but authorities have since pledged to pick up their speed.
President-elect Claudia Sheinbaum said her government planned to work on improving an early alert system, similar to what the country has with earthquakes.
Through Thursday, John is expected to produce 15 to 30 centimeters (6 to 12 inches) of rain across coastal areas of Chiapas state with more in isolated areas. In areas along and near the Oaxaca coast to southeast Guerrero, between 25 and 50 centimeters (10 and 20 inches) of rain with isolated higher totals can be expected through Thursday.
“You’re going to feel the impacts of the storm probably for the next couple of weeks to a couple of months,” meteorologist Benz added.